Crawled — Not Indexed & Navigating Google Ranking Fluctuations Post-Updates
Is your website crawled but not indexed by Google? This common issue, known as «crawled currently not indexed,» hinders your site’s visibility. Users can’t find your valuable content. This guide details how to fix crawled but not indexed scenarios. We’ll also explore ranking fluctuations on google updates. Learn to get pages indexed and stabilize your site’s search positions.
Understanding «Crawled — Currently Not Indexed» – Core Issues & Causes
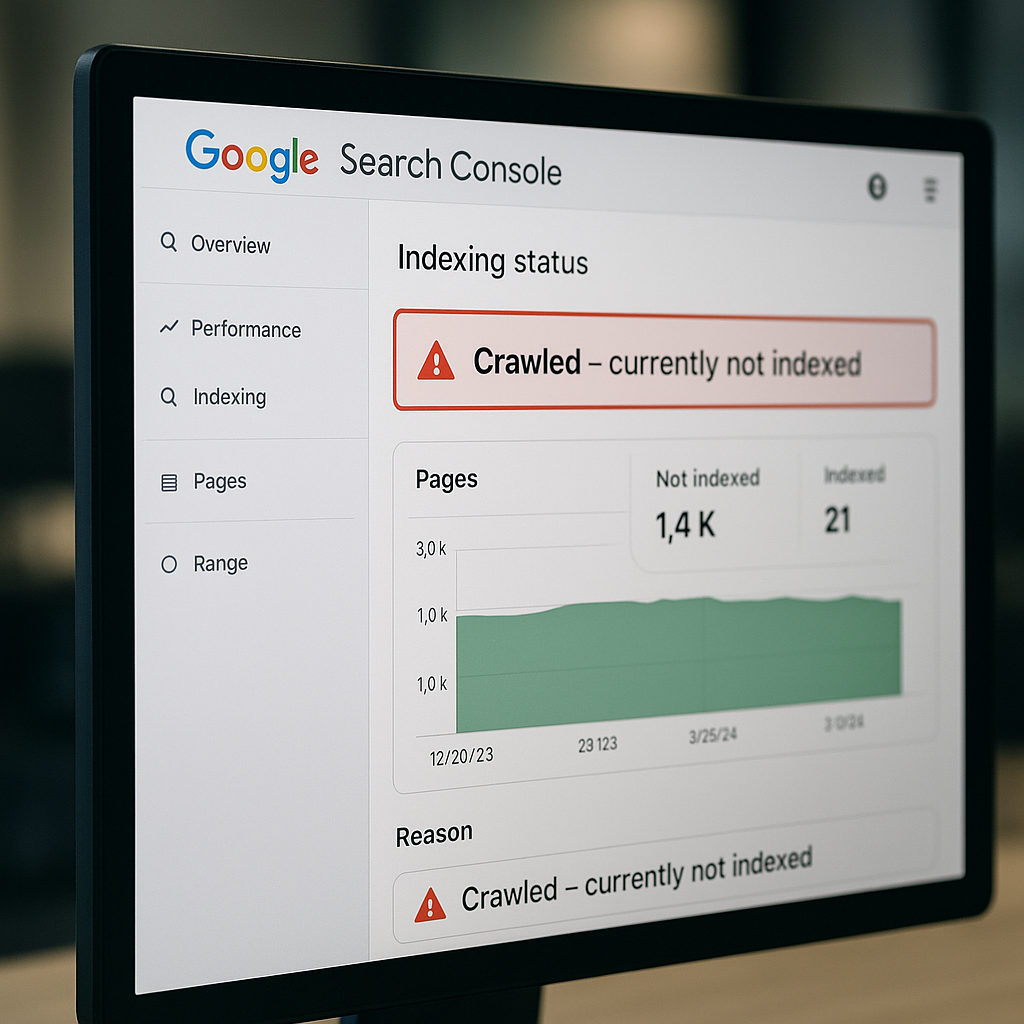
The «crawled currently not indexed» status within Google Search Console signals a significant problem. Googlebot has visited your pages. However, it hasn’t added them to its primary index. This situation demands immediate investigation.
One primary reason can be low perceived content quality according to Google. Algorithms like Panda and subsequent Core Updates analyze page value. Non-unique or unhelpful text is often disregarded by search crawlers.
Technical errors on your website also lead to the «crawled not indexed» status. Server-side issues or slow loading times, perhaps through CDNs like Cloudflare or AWS, can impede crawling. Improper JavaScript execution might hide crucial content from Googlebot.

Incorrect configuration of your robots.txt file or accidental use of the noindex meta tag is a frequent mistake. Webmasters sometimes inadvertently block important sections. Reviewing these files is a foundational step for a «crawled currently not indexed fix.»
Crawl budget issues are particularly relevant for larger websites. Google allocates finite resources for scanning each site. Numerous low-quality URLs can deplete this budget quickly. Consequently, important pages may be overlooked.
Duplicate content is another contributing factor. If Google encounters multiple versions of the same page, it will select one as canonical. Others might then receive the «google crawled but not indexed» status. Implementing canonical tags (rel=»canonical») helps resolve this ambiguity.
The absence of quality backlinks also plays a role. A site’s link profile is a significant trust and authority signal for Google. Pages lacking authoritative inbound links may be deemed less important by the search engine.
Navigating Google Ranking Fluctuations After Algorithm Updates
Google ranking fluctuations are a standard occurrence following major algorithm updates. Core Updates from Google, often announced via their official blog, frequently cause SERP volatility. This impacts a vast number of websites globally.
Every google rank fluctuation study and post-update analysis reveals shifts in ranking factors. Google continuously refines its algorithms. The objective is always to enhance the relevance and quality of search results for its users.
Ranking fluctuations on google updates can often be attributed to a re-evaluation of content quality. The E-E-A-T principles (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) are increasingly critical. This is especially true for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) websites.
A site’s technical health significantly influences ranking stability. Page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS security are fundamental requirements set by Google. Organizations like the W3C establish web accessibility and technical standards.
Changes in user behavior and evolving search intent are also factored in. Google analyzes this data, partly through tools such as Google Analytics. This influences which sites are deemed most relevant for specific queries.
The SEO efforts of competitors can also induce ranking fluctuations. If competitors substantially improve their sites and content, your positions might decline. This reflects the dynamic nature of SEO.
Penalties, whether manual or algorithmic, due to violations of Google’s guidelines are a severe cause of rank drops. These can result from low-quality link building or manipulative SEO tactics. Checking Google Search Console for notifications is essential.
Solving «Crawled — Not Indexed»: Methods Compared
Improving Content Quality
- Speed of Effect: Medium to Long-term
- Effort Involved: High
- Technical Knowledge: Low to Medium
- SEO Risk: Low
- Example Action: Rewriting content, adding expert insights, ensuring uniqueness. Focus on value for the user, adhering to Google’s quality rater guidelines.
Technical Site Optimization
- Speed of Effect: Medium
- Effort Involved: Medium
- Technical Knowledge: Medium to High
- SEO Risk: Low
- Example Action: Conducting a full technical SEO audit, fixing server errors (check AWS or Cloudflare logs), improving site speed, ensuring mobile-friendliness.
Correcting robots.txt / noindex
- Speed of Effect: Fast (after recrawl)
- Effort Involved: Low
- Technical Knowledge: Medium
- SEO Risk: Low
- Example Action: Reviewing and correcting robots.txt directives, removing incorrect noindex tags. Use Google Search Console’s tools for testing.
Crawl Budget Optimization
- Speed of Effect: Long-term
- Effort Involved: High
- Technical Knowledge: High
- SEO Risk: Low
- Example Action: Removing or noindexing low-value/duplicate pages, improving site structure, ensuring fast load times.
Implementing Canonical Tags
- Speed of Effect: Medium
- Effort Involved: Medium
- Technical Knowledge: Medium
- SEO Risk: Low
- Example Action: Adding rel=»canonical» tags to specify the preferred version of duplicate or similar pages.
Requesting Re-indexing in GSC
- Speed of Effect: Fast to Medium
- Effort Involved: Low
- Technical Knowledge: Low
- SEO Risk: Low
- Example Action: Using the «Request Indexing» feature in Google Search Console for individual URLs (use sparingly).
Utilizing Indexing Services
- Speed of Effect: Potentially Fast
- Effort Involved: Low
- Technical Knowledge: Low
- SEO Risk: Medium (if service uses non-compliant methods)
- Example Action: Submitting URLs to a reputable service like SpeedyIndex, which aims to accelerate Google’s discovery. Always vet services carefully.
Key Actions for Stabilizing Rankings After Google Updates
- Analyze Google’s Guidance: Carefully review official communications from Google regarding the nature and focus of any algorithm updates.
- Prioritize E-E-A-T: Continuously enhance the Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness of your content and website.
- Conduct Technical Audits: Regularly eliminate crawl errors, improve page load speed (leveraging CDNs like Akamai or Cloudflare if appropriate), and ensure flawless mobile usability.
- Optimize User Experience (UX): Focus on intuitive navigation, content readability, and positive behavioral signals.
- Maintain a Healthy Link Profile: Regularly analyze and refine the quality of your inbound and internal links.
- Monitor Competitor Performance: Observe competitors who may have gained positions to identify potential areas for your own improvement.
- Ensure Content Freshness & Relevance: Keep your information up-to-date and aligned with current user needs.
FAQ: Addressing Your Indexing & Ranking Questions
- My page shows as «crawled — currently not indexed» despite unique content.
- Google may delay indexing unique content if a site is new, has low authority, or if the page is poorly interlinked. Technical glitches or insufficient crawl budget also contribute. Review your Google Search Console reports thoroughly (standard practice for 2023-2024).
- How quickly can «crawled currently not indexed» be fixed?
- The resolution time varies. Technical fixes (like robots.txt or noindex errors) can show results within days after Google’s next crawl. Content quality and link profile improvements are longer-term processes. Reputable indexing services like SpeedyIndex can expedite Google’s re-evaluation.
- Are ranking fluctuations on google updates always permanent?
- Not always. Some fluctuations can be temporary as Google’s algorithms fully roll out and recalibrate after a major Core Update. However, consistent drops signal a need for in-depth site analysis against Google Webmaster Guidelines.
- What tools besides Google Search Console aid in diagnosing indexing issues?
- For comprehensive analysis, paid tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Screaming Frog SEO Spider are invaluable. They assist in identifying technical errors, analyzing link profiles, and assessing content. Server logs from providers like AWS can also offer insights into bot access.
Glossary: Key Indexing & SEO Terms Explained
- Crawled — Currently Not Indexed: A status in Google Search Console indicating Googlebot has visited a page but has not added it to the search index.
- Googlebot: Google’s web crawling bot that discovers and scans web pages.
- Indexing: The process where search engines like Google analyze, categorize, and store information about web pages in their database (the index) to make them discoverable in search results.
- Ranking Fluctuations: Shifts in a website’s positions in Google’s search results, often observed after algorithm updates.
- Google Search Console (GSC): A free service from Google that helps webmasters monitor their site’s indexing status and performance in Google Search.
- E-E-A-T: Stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness – criteria Google uses to assess content quality, especially for YMYL topics.
- Crawl Budget: The finite amount of resources (time and number of URLs) Googlebot allocates for crawling a specific website.
- robots.txt: A file on a web server that instructs search engine crawlers which pages or sections of the site should not be crawled or processed.
- noindex: A meta tag or HTTP header directive that tells search engines not to include a specific page in their index.
- Core Updates: Significant, broad changes to Google’s core ranking algorithm.
Common Mistakes & What to Avoid in Your Indexing Strategy
- Neglecting Google Search Console: Failing to regularly monitor «Coverage» reports and error messages is a critical oversight.
- Superficial Content Analysis: Publishing «thin» or non-unique content that doesn’t solve user problems is a primary reason pages remain «crawled not indexed.»
- Incorrect robots.txt Blocking: Accidentally disallowing important pages or entire site sections from being crawled.
- Overuse or Misuse of noindex: Applying the noindex tag to pages that are intended for search visibility.
- Ignoring Page Speed and Mobile-Friendliness: These are crucial ranking and indexing factors for Google according to current (2024) standards.
- Sole Reliance on Indexing Services: Forgetting that such services assist discovery but don’t fix fundamental quality or technical site issues.
- Acquiring Low-Quality Backlinks: This can lead to negative google ranking fluctuations and even manual penalties.
- Panicking After Every Google Update: Instead, analyze changes methodically and adapt your strategy. Organizations like the IETF continuously evolve web standards, and Google aligns
Expert Opinions on Indexing & Ranking Stability
- Dr. Eleanor Vance, Digital Strategy Analyst :
«The ‘crawled — currently not indexed’ phenomenon typically signifies that Google’s algorithms perceive a deficit in unique value proposition for the user on a given page, or they are encountering technical impediments to full content rendering or access. Comprehensive google rank fluctuation study consistently reveals that following algorithm updates, websites that prioritize and demonstrate sustained investment in content quality and superior user experience achieve greater stability. Conversely, reactive attempts at a quick ‘crawled currently not indexed fix’ without rectifying foundational issues rarely yield lasting results. Sustainable SEO performance is an iterative process of refinement, not a singular event.» - John «JP» Peterson, SEO Consultant :
«Look, Google wants to index everything good and easy to get to. If your pages are getting the ‘google crawled but not indexed’ tag, first thing you gotta do is check your Google Search Console – make sure Google can actually see your stuff properly. Then, be honest with yourself: is your content actually useful and different? No amount of fancy tricks or third-party pushing is gonna make Google love a dud page. Their bots are smart; they look for real quality.» - Aisha Khan, Lead Content Strategist at «DigitalPeak Insights»:
«What we’re seeing a lot with ranking fluctuations on google updates, especially in the 2023-2024 period, is that sites really need to nail their E-E-A-T – that’s Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Google is doubling down on making sure search results are reliable, particularly for important topics like finance or health (YMYL). If you’re not clearly showing you’re an expert and can be trusted, you’re going to feel those ranking shifts more. It’s not just optional anymore; it’s a must-have for staying visible.»
Take Control of Your Indexing
Resolving indexing problems and navigating Google’s ever-evolving algorithm updates requires a comprehensive, informed approach. Eliminating the «crawled currently not indexed» status and achieving stable rankings begins with a thorough analysis of your website’s technical health, content quality, and authority signals.
Don’t let your valuable content remain invisible to your target audience. Start by auditing your website and diligently reviewing your Google Search Console data. If you’ve addressed the fundamentals and need assistance in accelerating the discovery and re-evaluation of your optimized pages, SpeedyIndex is equipped to provide effective solutions. Learn how to fix crawled but not indexed issues and regain your search visibility with our support and tools.








Hi,
Google Search Console’s index coverage report often flags pages as «crawled but not indexed,» and your breakdown of technical fixes is spot-on. One angle worth exploring is how Core Web Vitals impact this—pages with poor LCP or CLS scores might get deprioritized, as Moz’s 2023 study showed a 12% drop in indexing for slow-loading pages.